This week let us talk about Stock Options.
What are Stock Options?
To understand what a Stock Option means, you must first understand the words “stock” and “Option”.
What is a Stock?
A stock represents a share of ownership in a company. Every company, public or private, has an owner(s) or shareholders who have been allocated shares. Shareholders own the company to the extent of the shares they hold. Thus, if I form Ohafia Tech with 100,000 registered Shares, and I allocate 50,000 shares to my partner Anne in exchange for N50,000, Anne now owns 50% of the Ohafia Tech.
This also means I have set a value of Ohafia Tech at N100,000 because I was able to sell 50% of the shares for N50,000, thus one share of Ohafia Tech is N1, and the market capitalization of Ohafia Tech is N100,000. Market Capitalization is calculated as the number of shares (100,000) multiplied by the share price (N1). This is my valuation; it’s NOT the market value
What is an Option
An Option represents an opportunity but not an obligation to buy shares later but at a fixed price called the strike price. Options are called derivatives because they derive their value from something else, in this case, the already existing shares.
Using Ohafia Tech, I and Anne, the company’s shareholders can issue options on our stock. These options allow whoever we offer the right and opportunity to buy shares of Ohafia Tech at a future date we set, at a strike price.
Why Issue Stock Options? Why Not Just Issue Shares
Companies are created to take the initial equity capital contribution of the company’s owners, invest in land & labor and generate positive long-term returns for shareholders.
This means Anne and I have invested N100,000 to generate profits for the company’s shareholders. Ohafia tech is a FinTech company that seeks to scale a process to allow farmers to bank using text. To build this application, Ohafia Tech needs trained engineers; paying trained engineers will erode cash from the startup. A solution is to offer shares to the staff that we intend to hire. This way, the staff became potentially shareholders of Ohafia Tech in the future.
Let us assume we want to hire an Engineer called Mark. we make him the below offer for his consideration.
- Basic salary of N1,000 a month
- Stock Option of 10,000 shares, vested in 2000 shares every year, with full vesting in year 5, at a strike price of N10.00. The stock option is not transferable and will extinguish after 10years.
What does this all mean?
“Stock Option of 10,000 shares”: This means Mark potentially is an owner of 10,000 shares of Ohafia Tech
“To be vested 2,000 shares every year”: Mark will not get these 10,000 shares of Ohafia Tech at once; instead, he will receive 2,000 shares annually. Thus, he gets the total shares in five years.
“At a strike price of N10.00” is the most critical information, Mark not only receives 10,000 shares in five years, but he buys those shares at N10 in five years from today. Yes, it’s not free. The deal is simple, at whatever price the shares of Ohafia Tech are in five years, Mark can buy them for N10. Options Are usually priced at a discount when issued.
Why Do Companies Offer Stock Options?
- To attract the high-quality staff: Mark has technical degrees and lots of qualifications; to pay him will eat up cash, so make him a part-owner to sweeten the attractiveness of Ohafia Tech
- To retain staff: by stretching the vesting period to five years before the total 10,000 shares are vested, Ohafia Tech can keep Mark for five years as an employee
- Motivation, Mark can buy shares of Ohafia Tech in Five years for N10. Thus, he is motivated to work hard and develop software that grows revenues of Ohafia Tech, which drives the valuation of Ohafia Tech
Why Should Mark Forego Cash For Options?
Options are usually given as an attractive remuneration package, especially for startups. Mark essentially can ask to receive a fixed cash salary. In effect, he can play it safe and get paid today; like he was buying a bond. However, if Mark accepts stock options, he is essentially buying stock. It’s not guaranteed that he can lose everything, but if the company becomes successful, he participates in its profits.
How Do Options Work in Practice?
There are two scenarios for options.
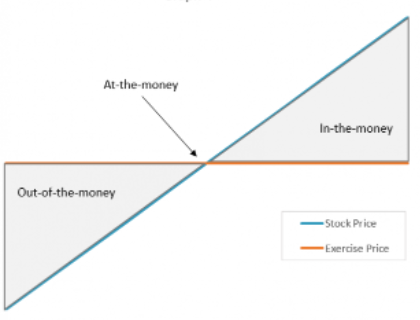
- In the Money, let us assume that Ohafia Tech launched its products to the market, and they became wildly successful, and the share price rose steadily from N1 to N50 in five years. This means these Options are “in the money” or have appreciated and have value. Mark can exercise his option to buy 10,000 shares at N10, not at the market price of N50. Thus, he makes a profit of N40 on each share and N40,000 in total. Marks’ decision to accept the stock options was a good call in this instance.
- Out of the money: on the flip side, let’s assume that Ohafia Tech was not able to break into the market and win market share despite its best efforts. Its shares thus fell from N1 to N0.20k a share. This means the options are now “out of the money”. Mark will not exercise his options because his choices are priced at N10, which is higher than the current price of N0.20k
In summary, options are derivates that give the right but not the obligation to take an action. They are helpful to attract and retain talent and motivate holders to seek to perform actions that will boost market prices.
Options prices are a very complex subject, especially for private non-listed company shares, make sure you are consulting with your financial adviser before making any decisions.




Comments are closed.